-
- software
FastReact 1.0
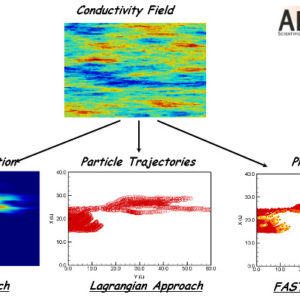
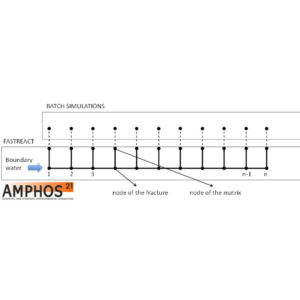
- Reactive transport modelling is commonly used to provide support for repository engineering activities and safety assessment studies. Yet, the very large temporal and spatial scales involved in these types of studies along with the non-linearity of the underlying processes pose formidable computational challenges that usually force modellers to simplify the problem. In order to circumbent these limitations, we…
- Leer más
-
- software
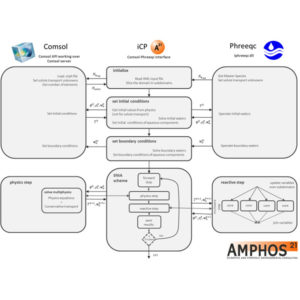
iCP
- iCP stands for interface Comsol-Phreeqc. It is an interface to couple Comsol and Phreeqc. The result of this interface is a tool for solving a wide range of multiphysics and chemical problems. It is written in Java and uses the IPhreeqc C++ dynamic library and the Comsol Java API. Furthermore, it takes advantage of the multicore computer architecture by balancing…
- Leer más
-
- software
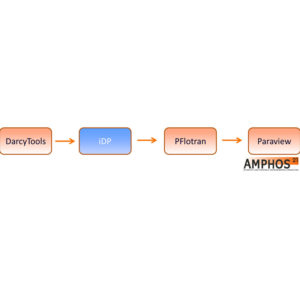
iDP
- iDP stands for interface DarcyTools-PFLOTRAN. It is an interface to couple DarcyTools and FLOTRAN. The main target is to develop an integrated reactive transport platform consisting of Darcy Tools (complex flow simulations) and PFLOTRAN (High Performance Computing for geochemical simulations) in order to incorporate DarcyTools (ability) with the reactive transport capabilities of PFLOTRAN such as the high performance computing (HPC)…
- Leer más
-
- software
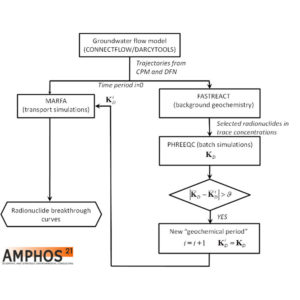
iFM
- With iFM we propose a novel approach that constitutes a significant improvement over the traditional constant Kd model, while at the same time allows simulations performed with MARFA to be carried out sufficiently quick to permit probabilistic analyses. The basic premise of this approach is that the “background” geochemistry (excluding radionuclides) will first be pre-calculated using a reactive transport code…
- Leer más
-
- software
iGP
- iGP is the interface between GiD and PFLOTRAN and is developed by Amphos 21. iGP provides a powerful and user-friendly pre and post-processing environment to PFLOTRAN. In iGP, the user can define different regions, set different materials, apply different boundary and initial conditions, mesh complex geometries (using structured, semi-structured or fully unstructured grids), run PFLOTRAN and post-process the results. License…
- Leer más
-
- software
iPP
- iPP is a coupling code interfacing two standalone software: Palabos and PhreeqcRM. The main goal of this development is the simulation of reactive transport processes in porous media at the pore-scale. Palabos (www.palabos.org) is an open source three dimensional (3D) CFD solver based on the lattice Boltzmann method. PhreeqcRM is an open source geochemical reaction module based on PhreeqC specifically…
- Leer más
-
- Sin categoría
MARFA
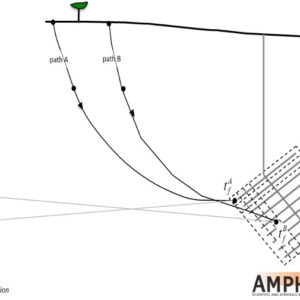
- The computer code MARFA (Migration Analysis for Radionuclides in the FAr field) uses an extremely efficient particle-based Monte Carlo method to simulate the transport of radionuclides in fractured rock systems. The algorithm uses non-interacting particles to represent packets of radionuclide mass. These particles are moved through the system according to rules that mimic the underlying physical transport and retention processes.…
- Leer más
-
- software GNU
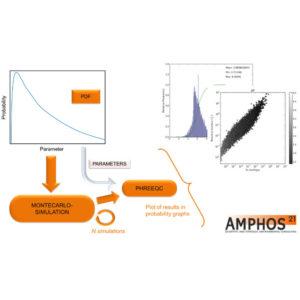
MCPhreeqc
- 0,00€
- MCPhreeqc 2.0 PHREEQC se utiliza para el modelado de diferentes tipos de procesos geoquímicos naturales. Lo que todos tienen en común es que hay una inconsistencia sobre el valor exacto de los parámetros utilizados. En el método de modelado clásico, el modelo se calibra para encontrar los valores "correctos" de estos parámetros. Otro enfoque consiste en aplicar modelos estocásticos utilizando…
- Añadir al carrito
-
- software GNU
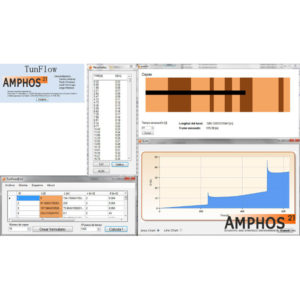
TunFlow
- 0,00€
- Las entradas de agua subterránea dentro de túneles pueden representar un peligro potencial, así como un factor importante que controla la velocidad de avance en la construcción de un túnel. Una de las principales dificultades prácticas que se asocian a menudo con la construcción de túneles tiene relación con las aguas subterráneas. Además, se necesitan predicciones de los flujos de…
- Añadir al carrito